Physiotherapists focus on how the body moves and functions through physiotherapy. They use their clinical skills and knowledge of psychology to assess patients and treat or reduce the risk of physical and cognitive disorders that impede a person's ability to perform regular daily activities.
Physiotherapy focuses on maximising quality of life and functional movement potential, working with the physical, psychological and emotional aspects as well. Physiotherapists help people overcome problems caused by disease or disabilities to improve their mobility and quality of life.
What is physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy (also Physical Therapy) is a healthcare profession concerned with human function and movement and its relationship to health.
Physiotherapy aims to treat, prevent and assist in the rehabilitation of injuries or disabilities through examination, diagnosis and treatment. The physiotherapist works closely with patients who have experienced sports injuries, orthopaedic conditions or neurological disorders, such as stroke or multiple sclerosis, helping them regain function after an injury or illness occurs. Physiotherapists also work in private practice treating non-medical problems such as musculoskeletal issues caused by repetitive strain injury (RSI), pain management for those suffering from chronic back pain, and so on.
Physiotherapists trained in the effects of disease and injury assess patients to diagnose disorders that limit people's ability to move and perform physical activity. They treat such conditions by developing an individualised plan based on each patient's specific needs.

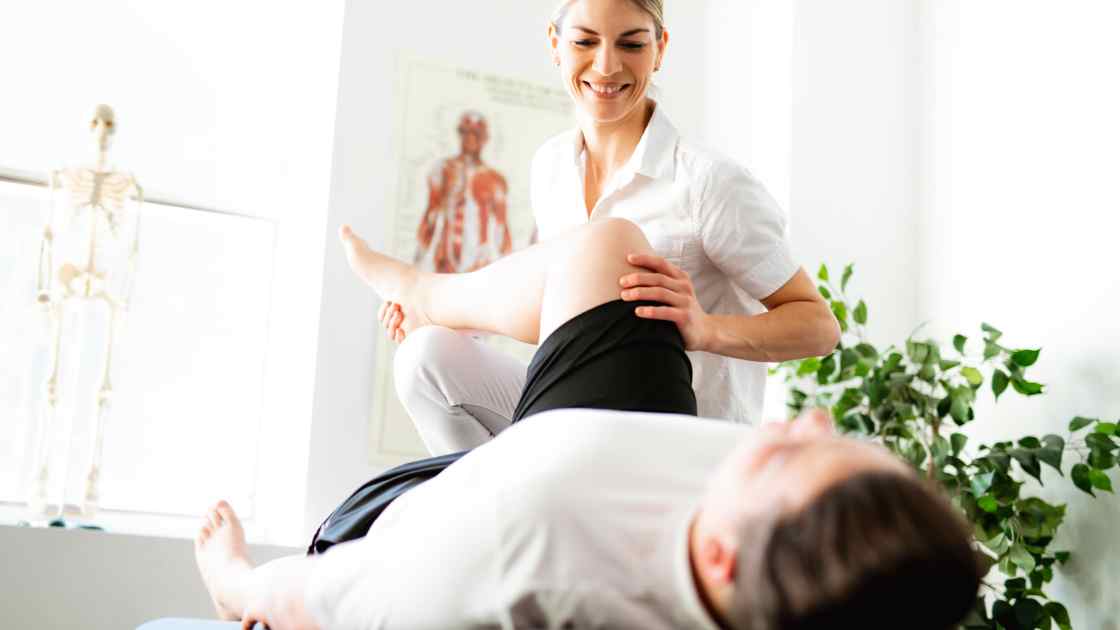
The Assessment
You’re in a lot of pain, and your doctor has referred you to see a physiotherapist. The physiotherapist will assess your symptoms, ask you questions about what happened and how it happened and then decide on the best way forward to help manage your pain.
Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximising quality of life and functional movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, treatment/intervention, habilitation and rehabilitation. This encompasses physical, psychological, emotional, social or spiritual aspects.
Physiotherapists help people overcome problems caused by disease or disabilities to improve mobility, function and quality of life. They use a wide range of techniques to do this including exercise, massage, manipulation (joints), hydrotherapy (swimming pool therapy), electrotherapy, and so on. Physiotherapists work in many different settings, such as hospitals, private practice clinics, and community health centres, among others.
Who Are Physiotherapists?
Physiotherapists help people overcome problems caused by disease or disabilities to improve mobility, function and quality of life. They are highly trained professionals who use a variety of techniques to help people recover from injury or disease. The treatments they provide vary depending on the individual, but can include:
- Osteopathy — using manipulation and massage to relieve pain in joints and muscles
- Exercise therapy — using exercises to improve strength, mobility, endurance and balance
- Massage therapy — applying pressure to specific areas of the body with different hand movements
- Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) — using short electrical pulses to stimulate muscles
- Traction — using gravity and weight to improve the flexibility and range of motion of your joints.
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) — using a stretching exercise that involves muscle spasms. You do this by contracting your muscles, then relaxing them, and then repeating the process over and over again.
When Should You See a Physiotherapist?
If you are experiencing pain or discomfort, you should visit one for diagnosis and treatment. If you are recovering from an injury, surgery or other procedures, you should see a physio before returning to your regular activities. Physiotherapists can also help patients with chronic conditions, such as arthritis or asthma. Finally, if you want to improve your general health and fitness levels but aren't sure which exercises will work best for you, visiting a physio may be helpful!
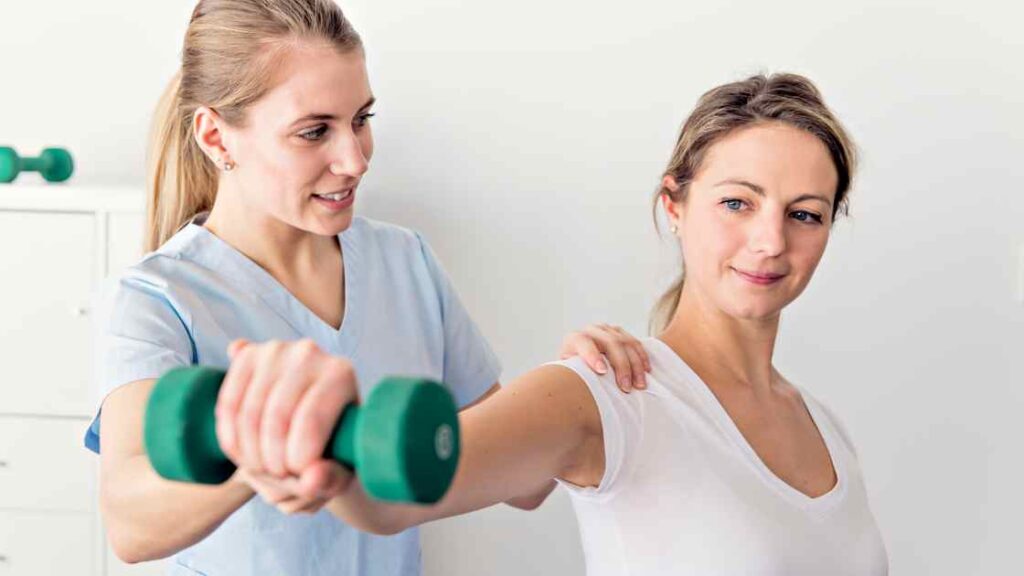

What can I expect at a physiotherapy clinic?
The first visit to your physiotherapist is an important one. It’s the time when you can expect to learn more about your condition and how it might be treated, as well as what to expect from the treatment itself. The physiotherapist will start by taking a detailed history of your problem, including information such as:
- The type of pain you experience (for example, acute or chronic)
- How long you have been experiencing the pain
- Any other symptoms or complications related to your injury
From this initial discussion, the physiotherapist will be able to formulate an appropriate diagnosis for you and decide if further tests are necessary. If so, these may include X-rays and blood tests. Once these initial investigations have been completed, treatment can begin!
What Does a Physiotherapist Do?
A physiotherapist is a health professional who specialises in the treatment of movement, function and performance relating to your body's structure and activity. They may also work with the respiratory system (which includes the lungs) and their disorders. Physiotherapists can help with any type of problem including back pain, arthritis and sports injuries. They can work in a variety of settings including hospitals, private clinics and community health centres. They may treat patients following surgery or accident injuries as well as those with long-term conditions like diabetes mellitus or chronic pain due to cancer treatment such as chemotherapy drugs.
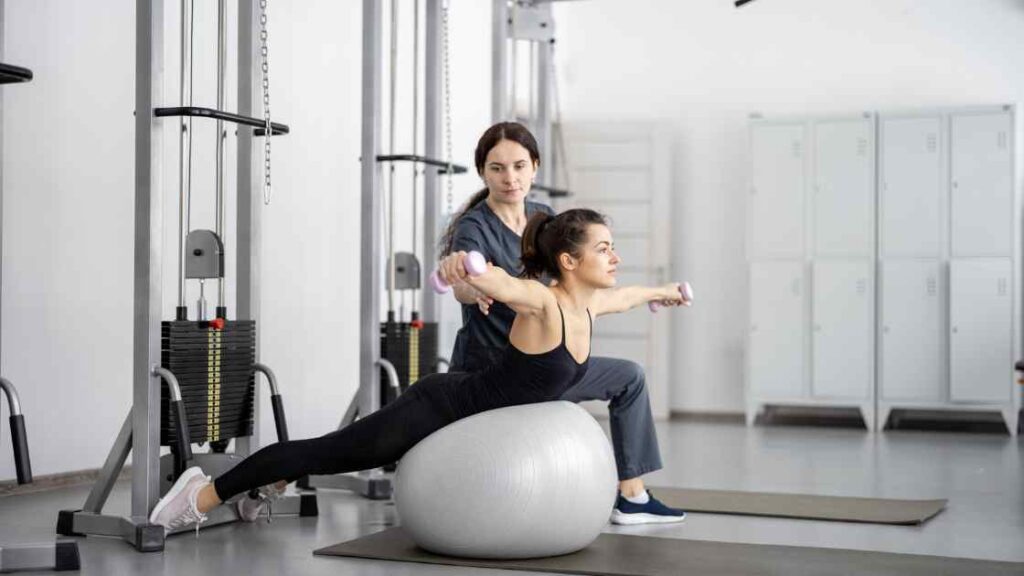

What Conditions Do Physiotherapists Treat?
- Musculoskeletal injuries: Physios help people recover from all kinds of musculoskeletal injuries, such as sprains and strains, tendonitis, and spinal problems.
- Arthritis: Physiotherapists can help treat osteoarthritis by teaching you exercises that improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Back pain: If you're suffering from chronic back pain (that's been going on for more than 12 weeks), a physiotherapist may be able to help you manage your symptoms so they don't get worse. They'll recommend exercises that strengthen your core muscles and improve posture, balance, coordination and flexibility—all things that can make a big difference in how much pain you're in when standing up or bending over in the shower.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: A condition caused by swelling inside the wrist leading to numbness or tingling sensations in the fingers is called carpal tunnel syndrome. It's common among people who type long hours at their jobs (like journalists).
- Fractures: A physiotherapist can guide what kind of splinting or casting you need after breaking a bone—and once those have been removed after healing has occurred!
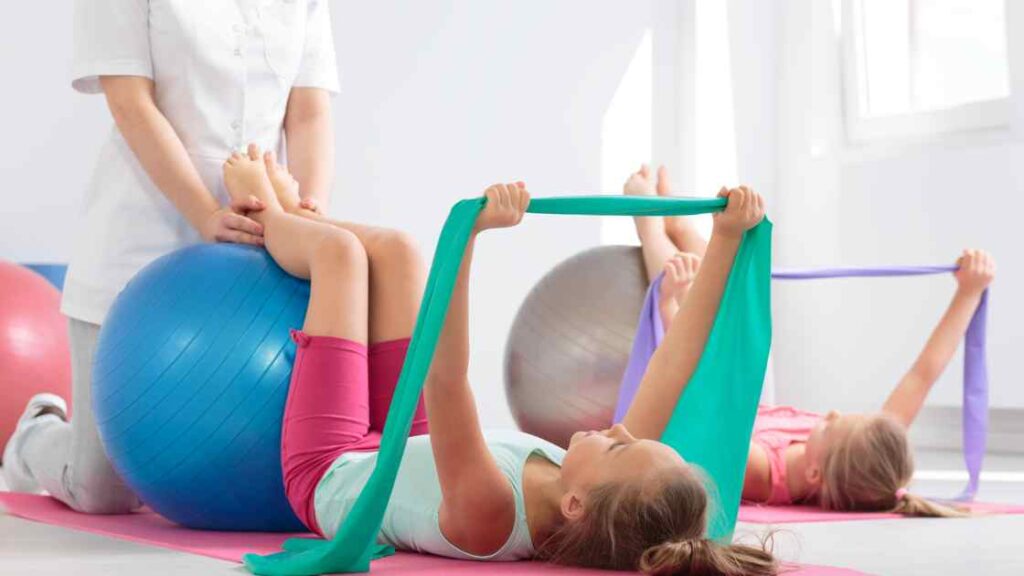

What is paediatric physical therapy?
Paediatric physical therapy is a branch of physical therapy that focuses on the treatment of children and adolescents with physical disabilities. The goals of paediatric physical therapy are to improve mobility, reduce pain and increase function. The focus is on specific exercises as well as education for parents and patients.
What is Physiotherapy at Home?
Physiotherapy at home offers all the benefits of a clinic at your residence. Home physiotherapy is a great option for patients who are unable to travel to the clinic. The service can be provided by either a physiotherapist or a trained and qualified health professional in your community. This form of physiotherapy is slightly more expensive than clinic visits but allows you more flexibility with your schedule.

What Are the Benefits of Physiotherapy at Home?
Here's a list of some of the awesome things about doing physiotherapy at home:
- You can do it whenever you want and whenever your body is ready. You don't have to worry about getting in and out of appointments or missing work because you were unable to get an appointment on the same day as your injury.
- There are no awkward interactions with other patients when you're recovering from an injury at home. You can just focus on healing!
Reasons to See a Physiotherapist
- To rehabilitate after surgery or an injury
- To prevent injury by working with a physiotherapist to develop or improve your movement patterns and strength.
- To prevent falls and improve your balance, coordination and reaction time. This is especially important if you're over 60 years of age.
- Because it's part of a healthy lifestyle—physiotherapy is often used in conjunction with other treatments such as massage therapy, acupuncture or osteopathy for people who want to improve their quality of life through better physical function.
Women’s Health-Related Physiotherapy
Women’s health-related Physiotherapy is one of the fastest-growing specialities in physical therapy. Physiotherapists who specialise in women's health are specially trained to help women with a variety of conditions including:
- Menstrual disorders
- Urinary incontinence (UI)
- Sexual dysfunction
- Pelvic pain and sexual dysfunction related to gynaecological surgery or cancer treatment Postpartum depression (PPD) and anxiety disorders
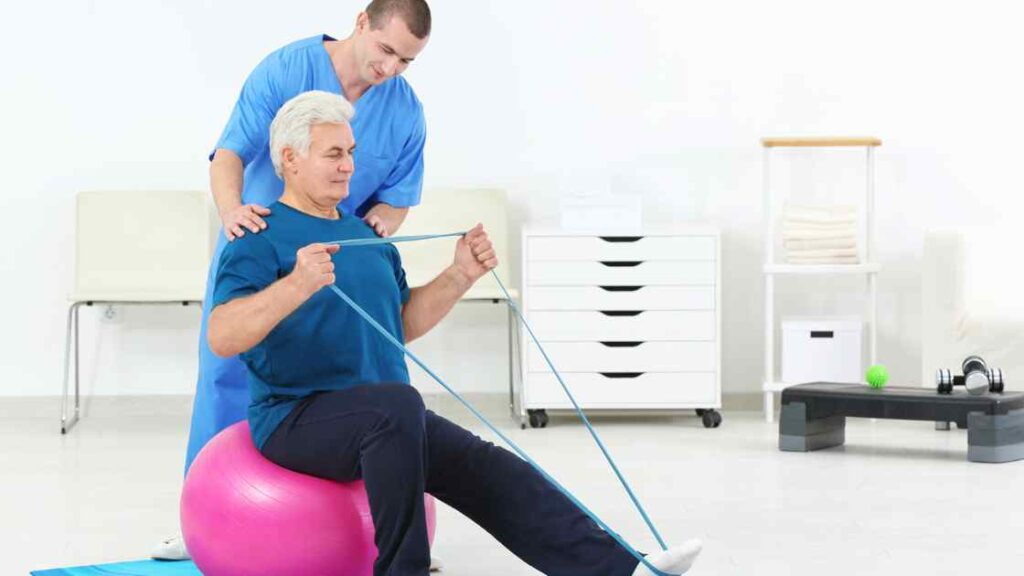

Geriatric Physiotherapy
The role of the physiotherapist is to help their aging patients recover and rehabilitate from injuries and illnesses. Geriatric Physiotherapy can be used in many settings, including hospitals, rehabilitation clinics, private practices, schools and sports teams.
Physiotherapists are highly trained professionals who specialise in physical therapy: they treat injuries using manual therapy (the manipulation or mobilisation of a joint), exercise rehabilitation or other therapeutic interventions such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
There are two main types of physiotherapists: orthopaedic and non-orthopaedic (also known as general). Orthopaedic practitioners treat musculoskeletal conditions through manual therapy for pain management; non-orthopaedic practitioners focus on general health care rather than one specific body system like bones & joints.
Neurological Physiotherapy
Neurological physiotherapy is a branch of physiotherapy that specialises in the treatment of neurological disorders and injuries. Neurological physiotherapists use manual therapy techniques, such as massage and joint mobilisation, to reduce pain and improve mobility in patients with neurological disorders or injuries. These techniques can be applied directly to the affected muscle(s), or indirectly by modifying factors that influence their functioning (e.g., posture). The goal is to restore optimal function and prevent further disability by restoring movement patterns on both sides of an injury so that full strength can be restored quickly after an injury occurs
Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy
Musculoskeletal physiotherapy is a branch of physiotherapy that specialises in treating people with musculoskeletal disorders and injuries. Musculoskeletal physiotherapists provide hands-on treatment to help improve mobility, function and quality of life. They also work with patients to prevent future problems from developing.
They may treat conditions such as:
- back pain
- muscle strains/sprains
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
Cardiorespiratory/pulmonary/vascular Physiotherapy
Cardiorespiratory physiotherapy is a type of physiotherapy that deals with the heart and lungs. The cardiopulmonary system includes these parts:
- Heart (blood circulation)
- Lungs (respiration)
- Blood vessels (transportation of blood)
The Cardiopulmonary system is responsible for the transportation of oxygen and nutrients to the cells, as well as the removal of waste products. The cardiopulmonary physiotherapist will assess your condition and determine which type of treatment is best suited for your needs. This can include: Breathing exercises (respiratory), Resistance training (cardiovascular), and Muscle strengthening exercises.
Rehabilitation and Pain Management
Physiotherapy is a treatment that helps you regain the strength, movement and function of your body. It is often used to treat people who have had an injury or illness, but it can also be used to prevent injuries. Physiotherapists work with patients to help them improve their condition through exercise and gentle mobilisation techniques. A physiotherapist may also advise on how best to manage pain caused by an injury or condition. They may recommend certain activities or rest until the pain subsides before resuming normal activities again. Physiotherapy can be used to treat a wide range of conditions, including back pain and neck pain, headaches, dizziness and migraines, sports injuries, muscle strains or sprains.
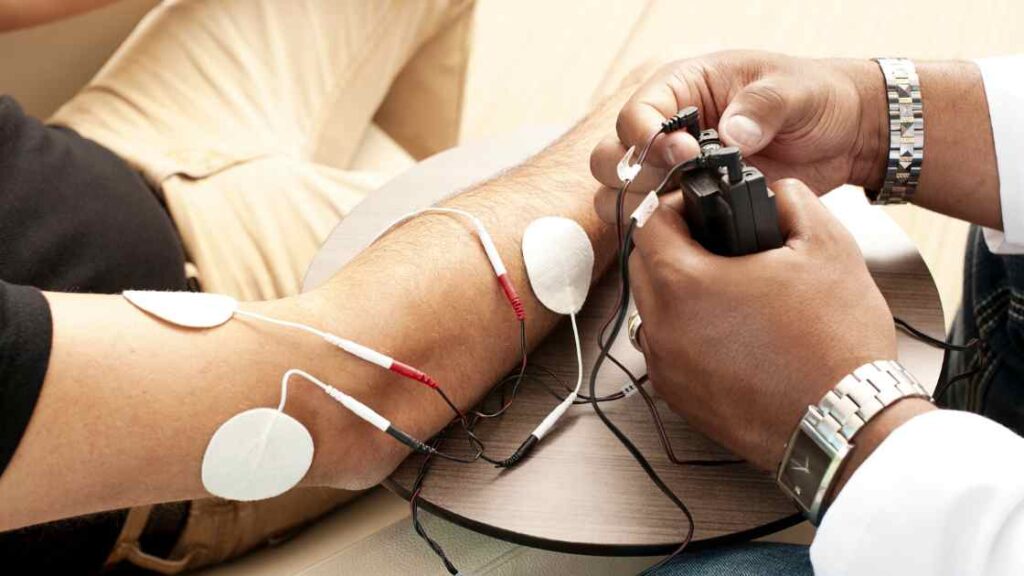

Sports-Related Physiotherapy
Sports-related physiotherapy is a branch of physiotherapy that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of injuries sustained by athletes. It is one of the most highly specialised areas within physiotherapy, with professionals who are specifically trained to treat sports-related injuries.
Sports-related physiotherapists work with athletes both before and after their sporting event, helping them recover from their injury in time for their next match or workout. They may also help educate athletes on how to prevent further injury from occurring through stretching programs, exercises and other techniques.
A sports-related injury can be anything from a strained muscle to a broken bone. The severity of the condition will determine how long it takes for an athlete to recover and return to their sport, but in some cases, physiotherapy is not enough and surgery may be required.
Benefits of Physical Therapy
Physiotherapy is a medical speciality that uses physical methods to treat patients with neuromusculoskeletal issues and suffering from postural collapses. Physiotherapy can help people suffering from various health-related problems like joint pain, back pain, muscle spasms, nerve and spinal cord injuries etc., by applying various therapeutic approaches, such as manual therapy (massage), electrotherapy (TENS), hydrotherapy (water therapy), and so on. Physiotherapists also help companies buy the right kind of ergonomic equipment for their staff to keep the right posture. Ergonomics in physiotherapy is just as important in this paramedical field.
Physiotherapists work under the supervision of doctors who refer patients for their treatment. Physiotherapy aims to improve movement and reduce pain in the joints or muscles by using exercise programs that are designed specifically for each patient’s problem area.
Physical therapists are experts at treating a wide range of conditions affecting muscles and nerves including arthritis, torn ligaments/tendons/ligaments, sprains/strains/muscle strains/muscle sprains/muscle tears. They may also include symptoms, such as back pain, sports injuries, neck pain, rotator cuff injuries, tendon tears, labral tears or SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior) lesions.
These conditions can be caused by wear-and-tear type of degeneration within an older population due to repetitive overhead motions, such as throwing baseballs etcetera. In addition, they use many other techniques, including ultrasound machines which send sound waves into tissues causing vibration to stimulate blood flow into injured areas for faster healing. This technique will also protect the healthy tissue around the area and increase circulation while decreasing the swelling. Remember, too much heat exposure can cause permanent damage, so don’t use heating pads over long periods even though they feel good right now because heat increases blood flow which will increase bleeding around injury sites.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy is a great way to help with any pain you may be experiencing. It can be used for many different purposes and many different treatments can be used. The most common type of physiotherapy treatment will involve stretching, strengthening exercises and massage which are all designed to improve your mobility and posture. One example of physiotherapy involves a specialised exercise programme which focuses on improving your function after injury or surgery along with pain management techniques, such as heat packs or ice packs depending on the type of injury.
FAQs
Will physiotherapy help tennis elbow?
Yes, it will help. Physiotherapy is known as a non-invasive form of treatment, and it's been proven to work for many different types of injuries. The therapy can be done at home or in a clinic, depending on the severity of your condition.
Should physiotherapy hurt?
No! If you're experiencing pain during your treatment, it means that something isn't working properly; so discuss it with your physiotherapist immediately!
Is physiotherapy a paramedical course?
Yes. It is an important part of the medical field as it helps in reducing pain and helping people recover from disabilities.
Can you do physiotherapy when pregnant?
Yes. However, there are certain precautions that need to be taken before starting this course. Your doctor should be consulted first if you are pregnant.
When should you stop physiotherapy treatment?
Physiotherapy treatment should be stopped when there is no improvement in your condition after three months of treatment or if you have recovered completely from your ailment without any further treatment.
Are physiotherapists doctors?
No. Physiotherapists are not doctors, but they do need to be registered with a governing body.
Can physiotherapy cure paralysis?
No. Physiotherapy cannot cure paralysis, but it can help to improve mobility in patients who have suffered from a spinal cord injury or stroke.
What is an ideal posture?
An ideal posture is one that is comfortable and balanced. This means taking into account factors like weight distribution, flexibility, range of motion, and strength levels.
Can physiotherapy help sciatica?
Yes! Physiotherapy can help sciatica by addressing the underlying cause of the pain, which may be due to poor posture or muscle imbalances in the lower back and hips.
How can physiotherapy help with recovery?
Physiotherapy can help with recovery by helping patients regain strength and flexibility after an injury or illness has occurred. It also helps patients learn how to manage their symptoms more effectively so they can return home sooner than expected.
Does physiotherapy help stroke patients?
Yes! Physiotherapy has been shown to improve motor function and hand dexterity after a stroke. It also helps patients learn how to perform daily activities, such as dressing themselves without anybody's help.
Will physiotherapy help plantar fasciitis?
Yes, physiotherapy can help in treating plantar fasciitis as it increases blood flow to the foot and reduces inflammation by massaging and stretching the muscles around the foot.
Can physiotherapy make things worse?
No, physiotherapy will not make anything worse unless you have a pre-existing condition that may be aggravated by physiotherapy treatment, such as osteoporosis or arthritis. Physiotherapy can make things worse if it's not done correctly. For example, if you have a back injury and the therapist pushes too hard or in the wrong direction, that can increase inflammation in your muscles and joints, making it harder for them to heal properly.
Why is physiotherapy contraindicated in fever?
Physiotherapy won't work if you have a fever because high temperatures make your body least competent to respond to treatment.
Can physiotherapy help with arthritis?
Yes, it can help with arthritis because it reduces swelling and pain which are both symptoms of arthritis. It also increases range of motion so that activities are easier on joints affected by arthritis which leads to less stress being placed on them while performing daily tasks, such as walking long distances or lifting objects.
Should I study physiotherapy or occupational therapy?
You should study both occupational therapy (OT) and physiotherapy (PT) because both focus on helping people with disabilities gain independence through movement and exercise. If you have to choose one over the other, do what you feel is right for you — there's no right or wrong answer here!
Will physiotherapy be in demand in the future?
Yes, physiotherapy is a growing and lucrative career option for students who want to work with people and help them achieve their health goals. Physiotherapists help patients recover from injury or illness by using physical interventions, such as exercise, massage, heat treatments, and hydrotherapy. The field of physiotherapy is expanding rapidly as more people are seeking out treatment for chronic conditions such as arthritis and back pain.
Is physiotherapy covered by insurance?
Physiotherapy is covered by many insurance plans because it's considered a medical service. If you're insured by your employer or have a private health plan, you should be able to get your therapy sessions covered by your insurance company. However, if you're not sure whether your insurance will cover what you need or how much it will cost out of pocket, check with your provider before making an appointment with a physiotherapist so they can let you know what options are available to you.
Does physiotherapy need a Neet test in India?
No. Candidates don't need to pass the National Eligibility-Cum-Entrance Test for admission into Bachelor of Physiotherapy courses; separate entrance exams are conducted instead.

